Eco Dobutamine
Holter
Stress Test
Drawingtamine echocardiography is another cardiac diagnostic procedure to identify the chances that a person has of having a heart attack or to define the conditions in which they are if they already have a known heart disorder. In most cases, it is used for the same purpose as the stress echo, except that the dobutamine echo is typically used in people who, for various reasons, are unable to exercise on the treadmill. It consists of recording images of the movement of the heart before administering dobutamine, images that will be compared with those that are recorded later, while dobutamine diluted in intravenous solution (serum) is being administered. Dobutamine causes acceleration and increased force of the heartbeat.
Echo Color Doppler
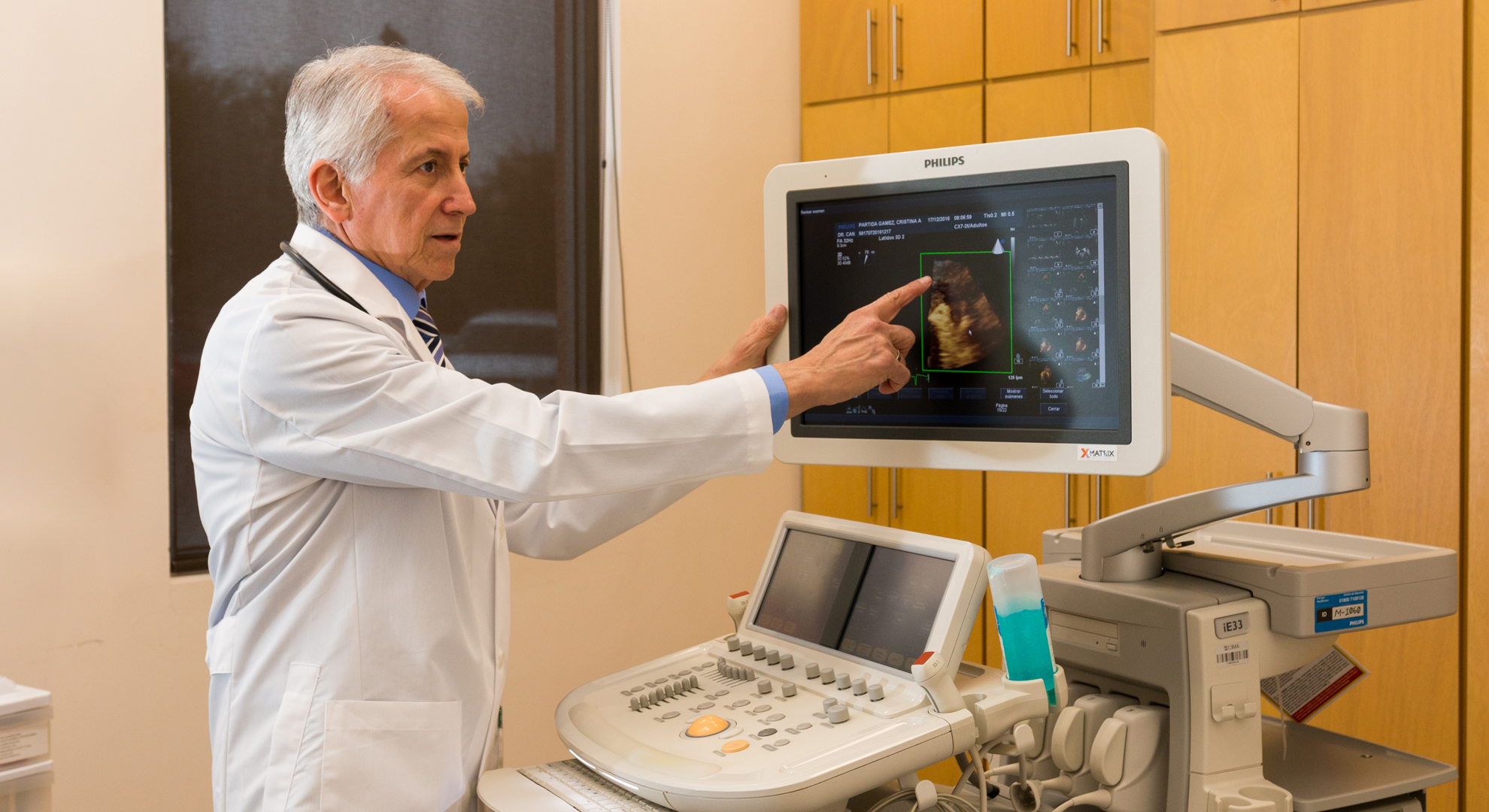
The color Doppler echocardiogram is a procedure to study a wide variety of disorders of the heart. It consists of viewing the heart through ultrasound, for which a small device is placed on the skin of the chest and it moves to see the different structures of the heart on a screen. In the images obtained, the cardiac structures are measured, their mobility is analyzed and the characteristics of the blood flow through the heart cavities and valves and the great vessels (arteries and veins connected to the heart) are investigated. The echocardiogram is a widely used procedure in daily practice as it offers great advantages for clinical diagnosis without involving any discomfort or risk for the patient.
Effort Echo
The stress echocardiogram is the combination of two ways to study the heart: the stress test and the echocardiogram. It is generally used to know the chances that a person has to suffer a heart attack or to estimate the prognosis if they already have a heart disorder, with the advantage that it offers more diagnostic power than the stress test alone. Before exercising on a motorized treadmill, images of the heart are recorded, which will be compared with the images recorded later, immediately at the end of the exercise, with the heart already racing.
Transesophageal Echo
The transesophageal echocardiogram consists of studying the heart using ultrasound, through a flexible probe that is introduced into the esophagus through the mouth. This probe has, at the tip, a small device that emits ultrasound and, since this device is just behind the heart, separated from it only by the wall of the esophagus, then the images obtained are of high quality and precision. The transesophageal echocardiogram is used to study a wide variety of heart diseases. The pharynx "throat" is usually sprayed with a local anesthetic to make tube transit more tolerable, and sedation is commonly used commonly guided by an anesthesiologist, as is often done in gastrointestinal endoscopy studies.
Resting Electrocardiogram
The resting electrocardiogram is the most widely used cardiac diagnostic study in daily practice. It consists of analyzing the electrical activity of the heart in order to identify changes or abnormalities that are usually found in many different heart diseases. The procedure is very simple and fast, also without any discomfort or risk for the patient. While the patient is lying down, terminal wires are connected to the skin of the arms and legs, as well as to the skin of the chest; These wires carry the electrical signals that the heart generates with each beat and are usually recorded graphically on a strip of paper that comes out of the EKG machine. The result is usually obtained immediately.
Holter
The Holter study consists of recording the electrocardiogram of a person while they carry out their daily activities. The recording, which most of the time lasts 24 continuous hours, is carried out on a small electronic device that is most commonly placed on the patient's waist and from which thin cables come out that are carried under the clothing to the chest and they are attached to patches that are attached to the skin. The purpose of the Holter study is, in the vast majority of cases, to investigate what type of cardiac arrhythmias a person has; This test is frequently ordered when there are palpitations (beats felt in the chest or neck) or when a cardiac exam reveals heart rhythm disturbances.
Stress Test
The stress test consists of observing what changes occur in a person's electrocardiogram as their heart races when they do physical exercise on a motorized treadmill. Based on the changes seen on the electrocardiogram, the likelihood of that person having a heart attack in the future can be seen. Before starting the exercise on the treadmill, an electrocardiogram is obtained that will be used to compare it with several electrocardiograms that will be obtained during the course of the exercise. The level of effort increases as the test progresses and the exercise is usually carried as far as the patient will tolerate. Once the effort is over, the person continues to be observed for a few minutes until full recovery. The stress test is one of the most widely used cardiology diagnostic procedures in the world.
Tilt Test
The tilt or inclined table test consists of placing the person on a tiltable “table” stretcher and taking him to an almost vertical position but always remaining somewhat inclined, his feet resting on a pedestal, his body resting on the stretcher. In this position, her vital signs and EKG are closely observed. Sometimes some medication is administered to make the purpose of the test more ostensible, frequently a tablet of some simile of nitroglycerin under the tongue or sometimes some intravenous medication. The most common indication for the tilt test is to study some characteristics in people who experience certain types of fainting or fainting.

